What types of tonometers are there?
A tonometer is a special device for measuring blood pressure. The indicators are displayed immediately and provide complete information about the level of blood pressure and heart rate. Any deviations from the norm are manifested by unpleasant symptoms: headache, nausea, dizziness.
The modern market is pleased with various devices for measuring the indicators under consideration. They differ in the range of functions they perform, the accuracy of readings, dimensions and cost.
There are two types of devices: mechanical and electronic. The former are divided into semi-automatic and automatic. Fully automated devices are divided into two subtypes: shoulder-mounted and wrist-mounted. They all differ in type and order of measurement, and also have pros and cons. But automatic models are considered the most accurate and reliable. For home use, you can purchase any of them; it is important to consider the functionality of the device, its cost and reliability.
Mechanical
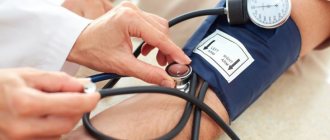
To find out which tonometer is accurate, pay attention to mechanical devices. They consist of a shoulder cuff, a pressure gauge and an air pump with an adjustable valve. Blood pressure readings are determined by listening to characteristic sounds through a stethoscope. In this case, blood pressure is measured by a person who has the appropriate skills, so this type of equipment is recommended for healthcare workers. It is often used in public health facilities such as hospitals. Which tonometer is more accurate - popular models:
- Healthcare CS-105. High-precision mechanical device in a metal case from CS MEDICA. There is a built-in phonendoscope, a cuff (22-36 cm) made of nylon with a fixing metal ring, an elastic bulb with a needle valve and a dust filter. The kit includes a case for convenient storage of equipment. Relatively cheap (870 RUR).
- Healthcare CS-110 Premium. A professional device, the pressure gauge of which is combined with a bulb. Made in a shock-resistant polymer case with chrome coating. An enlarged cuff (22-39 cm) is used without a fixing bracket. There is a large and easy-to-read dial, a pleasant-to-touch pear with a chrome-plated release valve. The measurement accuracy is confirmed by the European standard EN1060. It costs more than its analogues (RUR 3,615).
- Microlife BP AG1-30. This high-precision sphygmomanometer consists of a bulb, an air release valve, and a storage bag. A professional cuff (22-32 cm) with a metal ring is used. The model is popular among domestic doctors. A distinctive feature is the stethoscope head sewn into the cuff. It is inexpensive (1200 rubles).
Operating principle of the sphygnomanometer
When measuring, the stethoscope must be applied to the inside of the elbow. After this, the specialist needs to pump air into the cuff - he does this until, due to compression, the blood pressure level drops to 30-40 mm Hg. Art. greater than the estimated systolic pressure (upper limit) of the person being tested. The air is then released slowly so that the cuff pressure decreases at a rate of 2 mm Hg. per second.
Gradually falling, the pressure in the cuff reaches the patient's systolic value. At this moment, noises called “Korotkoff sounds” begin to be heard in the stethoscope. Diastolic pressure (lower) is the moment when these murmurs end. The operating principle is as follows:
- When the air pressure in the cuff is pumped up and exceeds the same parameter in the vessels, the artery is compressed to such an extent that the blood flow through it is suspended. At this time there is silence in the stethoscope.
- When the pressure inside the cuff decreases and the lumen of the artery opens slightly, the blood flow resumes. At this moment, Korotkoff sounds begin to be heard in the stethoscope.
- When the pressure stabilizes and the artery opens completely, the noise disappears.
How to Measure Yourself Pressure with a MECHANICAL Tonometer
Pros and cons of mechanical devices
Which tonometer is more accurate? When answering this question, a mechanical device is in the lead. Advantages of a mechanical device:
- impressive accuracy;
- affordable cost;
- reliable;
- suitable for measuring blood pressure even in patients with arrhythmia.
The main disadvantage is considered to be the difficulty of operation, especially for older people and patients with poor vision and hearing, impaired movement of the limbs - for them it will be a useless acquisition. To make it easier to measure blood pressure, some models include a cuff with a built-in phonendoscope head and a combined supercharger with a pressure gauge. For this reason, a sphygmomanometer can still be purchased for use at home.
- Intercostal neuralgia - symptoms on the left and right
- Proper breakfast
- Sberbank mutual funds - profitability and reviews. Rating of Sberbank mutual funds and how to make money on investments
The design of a mechanical tonometer and its operating principle
Mechanical devices are divided into mercury manometers and membrane ones.
How does a mercury manometer work?
Mercury manometer
The very first device for measuring indicators was a mercury mechanical one. Currently, it is practically not used. But it is considered the most accurate device for measuring blood pressure. It differs from modern ones by the presence of a mercury scale. Its column rises to the required number - this is blood pressure. The remaining devices do not differ from modern ones: a cuff attached to the shoulder, a pump for supplying air, a phonendoscope for capturing tones. The device is unsafe - if you move it carelessly, the scale with mercury can fall out and break, and the toxic liquid can spread across the floor. Therefore, this device was no longer used.
How does a mechanical membrane tonometer work?
Its operation is due to the presence of a sensitive part - a membrane. This is a flexible plate that bends under pressure and, under the influence of additional mechanisms, moves the needle on the pressure gauge scale. The device quite accurately displays the health status indicator, is safe and has a wide range of applications. It is considered a professional tonometer; all medical institutions are equipped with it. For proper use, skills are required; medical personnel are trained in them. At home, it is difficult to measure blood pressure on your own; the main difficulty lies in listening to tones.
Mechanical tonometer
The measuring procedure is as follows:
- Place the cuff on the forearm, slightly above the bend of the elbow.
- Place the phonendoscope on the vessel in the bend area.
- Inflate the cuff with air using a bulb.
- Gradually releasing air from the cuff with a special valve, listen to the tones and look at the arrow.
- The first “knocks” are systolic pressure.
- The final ones are the diastolic indicator.
Modern manufacturers simplify the design of the device. There are models with a phonendoscope inserted into the cuff. And some have a pear combined with a scale.
The advantages of a mechanical tonometer are listed by the following factors:
- low cost;
- high measurement accuracy;
- simple device and durability of use.
The disadvantages of the device include:
- measurement requires special skills, keen hearing and good vision;
- it is difficult to measure without outside help, otherwise the indicators will be distorted;
- no additional features.
For home use, it is better to purchase another type of tonometer.
What is the difference between an automatic tonometer and a semi-automatic one?
An automatic tonometer is an independent device that pumps air into the cuff and takes medical measurements. To find out the pressure, the user only needs to attach a special sleeve to the forearm or wrist, and then press the button on the body. There is no need to pump air using a bulb, nor do you need to count your own heartbeats.
There is no need to manually inflate the blood pressure monitor cuff
Semi-automatic tonometers work on a different principle. All calculations and measurements are also carried out without user participation, the results appear on a small screen. Typically, tonometers display upper and lower pressure and pulse. But a person has to pump in air on his own. This is done using the bulb supplied in the kit; you need to press it quickly and often to create the required degree of compression in the attached cuff.
About electronic devices
Electronic devices are divided into semi-automatic and automatic. The principle of operation is similar, but there is a difference in use.
How does a semi-automatic blood pressure monitor work?
Semi-automatic blood pressure monitor
This type of device also has a bulb and cuff, but instead of a scale there is an electronic screen and buttons for control. It is quite similar to a mechanical device, but simpler to operate. You need to use a pear to fill the cuff with air, and then wait until the tonometer itself processes the signals and displays the indicators in large numbers on the display.
The tonometer operates on electricity or batteries. The device is compact, quite accurate in readings and equipped with additional functions.
The advantages of the device include the following features:
- good accuracy, error up to 3 mm Hg. st;
- average cost;
- no need to listen to “knocks” and follow the pressure gauge needle;
- compact, easy to carry with you;
- it contains few electronics and reduces the risk of breakdowns;
- equipped with functions such as heart rate detection and the ability to remember the time of the previous measurement.
The device also has negative sides:
- supplying air with a pear increases the risk of distortion in measurements, which is especially difficult for elderly people;
- there is a need to replace batteries; their discharge usually happens at the wrong time;
- There are also breakdowns that require repair in a workshop.
But it is still the most popular tonometer used in everyday life.
Electronic tonometer: what are its operating principles?
This is the most expensive device of all types of tonometers. The kit includes a cuff and an electronic device connected to it. As soon as the cuff is put on the forearm and the button is pressed, the electric pump built into the device pumps air into it. The entire measurement process takes place automatically, the sensors process the indicators and display them in a digital image on the display screen. Tonometers are quite fragile and require careful handling. Convenient to use and small in size. There is no need to ask for outside help, but just sit comfortably and relax. Can work from mains or batteries.
Automatic blood pressure monitor
Advantages of an electronic tonometer:
- they can measure blood pressure correctly, reducing the risk of incorrect readings;
- measurement error – 3-5 mm Hg. st;
- the procedure is quite simple and accessible to older people;
- small-sized device.
But the newest model of tonometers also has disadvantages:
- high price;
- presence of error;
- short service life.
New models of automatic tonometers have many different functions that allow you to track not only blood pressure. It is necessary to list only the most popular and widespread:
- the device reminds you of the time of previous use;
- presence of arrhythmia indicator;
- presence of an indicator of correct fastening of the cuff;
- shows the average result of several measurements;
- automatically turns off after finishing work.
There are other functions such as a calendar, clock, cuff inflation indicators and many others.
What is the difference between a semi-automatic blood pressure monitor and a mechanical one?
When considering the types of tonometers, one cannot ignore mechanical devices. The principle of their operation looks like this:
- the user attaches a cuff to a selected area of the body; it is usually placed on the forearm;
- The head of a phonendoscope is placed under the edge of the compression sleeve, closer to the elbow, and the arms are inserted into the ears;
- The user independently pumps air into the cuff through the bulb and then deflates it.
Mechanical tonometers are the most accurate, but require some practice in use.
While the sleeve on the forearm is unclenched, it is necessary to count the heartbeats, which are clearly audible through a phonendoscope. At the same time, you need to look at the readings of the mechanical pressure gauge; the needle of the device will show blood pressure.
The entire process of measuring blood pressure with a mechanical tonometer occurs manually, and the person must also determine the results himself. The difference between semi-automatic models is that the user only needs to force air into the compression sleeve through the bulb. But the electronic device will automatically calculate your pulse rate and pressure readings.
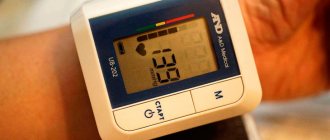
Electronic blood pressure monitor with wrist mounting
Among the electronic tonometers there is a model that measures pressure on the wrist. This device does not have a cuff, but is simply attached to the wrist, and indicators are displayed on the screen. For them to be accurate, having secured the device in place, you need to sit down and relax, holding your hand with the tonometer at chest level.
Wrist device
This model shortens the time needed to measure blood pressure and is ideal for athletes because they can monitor their readings during training. True, there is a drawback - this is a high error during the exercises. Doctors recommend using this model for people under 40 years of age. In the older generation, the vessels wear out, especially in the wrist area, which reduces the reliability of measurements.
Pros of a wrist tonometer:
- light weight and dimensions, you can carry it with you everywhere and always;
- easy to use, you don’t even need to undress;
- the ability to take measurements anywhere and even on the run;
- no need to select a cuff;
- has many functions available to a conventional automatic tonometer.
Disadvantages of a wrist tonometer:
- there are restrictions on use based on age;
- a very fragile device that requires careful use;
- when moving, it shows results with a large error;
- high price.
When purchasing this type of device, it is necessary to take into account the listed disadvantages and limitations.
Semi-automatic
Compared to a mechanical device, it has many differences, but has many similarities with an automatic one. In terms of price, the semi-automatic device is somewhere in the middle between the other two varieties. On sale you can find dozens of high-quality and durable mobile products of this type, among which the following have gained considerable popularity:
- Omron S1. A compact Japanese device for the shoulder, in which air is pumped using a rubber bulb. The results are displayed on a three-line display. There is a memory designed to store 14 measurements. The kit includes a logbook for recording data. The device is equipped with an indicator that flashes a signal on the display if the blood pressure level goes beyond the optimal range. Requires 2 batteries for power, no AC adapter. Cost – 1450 rub.
- Omron M1 Compact. Semi-automatic compact device for the shoulder, convenient and easy to use. Controlled with one button. There are all the necessary functions for quick and accurate blood pressure measurement. The memory capacity is designed for 20 measurements. Powered by 4 AAA batteries. There is no network adapter, it costs 1640 rubles.
- A&D UA-705. An upper arm device with the functions necessary for accurate and quick blood pressure measurements at home. There is an arrhythmia indicator, increased memory capacity that stores the last 30 results. Only 1 AA battery is needed to operate. The warranty lasts 10 years, but is more expensive than analogues - 2100 rubles.
How does it work
The semi-automatic device determines blood pressure and pulse in the same way as the automatic one. A distinctive feature is that the cuff must be inflated manually, i.e. rubber bulb. The list of their additional functions is more modest, but at the same time such a device has all the functionality necessary for measuring pressure. Many users and experts believe that a semi-automatic machine with a basic set is the best choice for home use.
Advantages and disadvantages
One of the disadvantages of the device is the need for manual pumping using a bulb, which is not suitable for weakened people. In addition, the accuracy of the data depends on the charge of the batteries and may also be affected by external influences. The advantages include:
- ease of operation compared to a mechanical analogue;
- affordable cost due to the fact that the device is not equipped with an electric motor, like an automatic model;
- The absence of an automatic air blower allows you to save money on the purchase and replacement of batteries.
How to choose the best one
Knowing what types of tonometers there are for measuring blood pressure, all their advantages and disadvantages, you can quite easily choose a device to use at home. Before you make a purchase, you need to know some nuances:
- What diseases does the patient have? The frequency of use of the device and its adaptation to the disease depend on this.
- Can the patient learn to use different types of devices?
- Price policy.
It is important to first decide which device you need: by operating principle or by installation location. It is better to buy a tonometer at a pharmacy or a special medical equipment store. First you need to check whether there are instructions in your native language, a warranty card, and a verification mark.
You also need to inspect the device for build quality, how all the parts are fitted, and the ease of opening and closing the battery compartment. Check all additional functions and ask your sales consultant to make the settings.
A mechanical tonometer guarantees the accuracy of pressure measurements and has a low cost, but it must be operated by a person with good hearing and able to learn how to operate the device. For elderly people who control their condition themselves, only an automatic tonometer is suitable. He does everything himself; he doesn’t even need to waste effort on inflating the cuff. If the patient has had a stroke or heart attack, or has arrhythmia, he must have the function of intellectual sensitivity.
Rating of the most accurate blood pressure monitors
To treat arterial hypertension (hypertension) and prehypertension (borderline state within 129-130/80-89 mm Hg), you need to find out which tonometer is more accurate and reliable. The market is saturated with a large number of offers: some models have high-speed measurements due to the non-decompression method, others are equipped with a sensor for the correct position of the hand (APS) with indication (sound, light), from others you can download data to a computer via a USB port, etc. Which tonometer is accurate - reviews of the best models:
| Model name and manufacturer | Country of Origin | Description | Operating principle | Price (rubles) |
| Shoulder | ||||
| AND UA 668 | Japan | Equipped with an LCD screen, a cuff 22-32 cm long. Controlled by one button. There is a memory of 30 cells. Powered by batteries (4xAA) and mains (adapter not included). Weighs 260 g. | Auto | 2629 |
| Omron M2 Classic | Japan | The set includes batteries, an AC adapter, and a journal for recording results. There is an Intellisense function, a high blood pressure indicator, a WHO scale, and a memory of 30 cells. The device produces an average value based on 3 indicators. | Auto | 2450 |
| Beurer BM 58 | Germany | Displays information on the LCD screen, is powered by 4 AA batteries and mains, but the adapter is not included. The number of memory cells is 60, there is an indication of arrhythmia, average value, WHO scale, connection via USB. Dimensions – 100x58x150 mm, weight – 364 g. | Auto | 3700 |
| Microlife BP A2 Basic | China | LCD screen, pulse measurement with an accuracy of 5%, cuff 22-42 cm, 4xAA batteries, memory for 30 cells, arrhythmia indication, motion indicator, WHO scale. Can be powered from mains, but adapter is not included. Dimensions – 82x57x135 mm, weight – 340 g. | Auto | 2300 |
| Omron HEM-700-E | Japan | Liquid crystal display, 4 batteries, 5 years warranty, 90-cell memory. Can be powered from the mains, but the adapter must be purchased separately. Total weight 490 g. | Auto | 2900 |
| A&D UA-705 | China | LCD screen, ability to measure pulse, powered by 1 AA battery, memory for 30 cells, arrhythmia indication, WHO scale. Controlled with one button. Weighs 120 g. | Semi-automatic | 1930 |
| Omron S1 | China | LCD screen, 2 AAA batteries, heart rate measurement, memory with 14 cells, air pump. Dimensions – 64x35x105 mm, weight – 80 g. | Semi-automatic | 1370 |
| CS Healthcare CS-105 | Japan (assembled in China) | Built-in stethoscope, sealing insert, storage case, dial pressure gauge, cuff 22-38 cm. Weighs 400 g. | Mechanical | 849 |
| Microlife BP AG1-30 | China | Built-in stethoscope, cuff 22-32 cm, dial pressure gauge, case-bag, without additional functions. Dimensions – 175x70x103 mm, weight – 450 g. | Mechanical | 820 |
| Wrist-mounted | ||||
| BEURER BC44 | Germany | Measures using the oscillometric method, operates only on batteries, and turns off after 1 minute of inactivity. Equipped with a large display with large numbers and a WHO indicator. The measurement results are stored in memory. The length of the cuff is 14-20 cm. Dimensions – 67x29x88 mm, weight – 98 g. | Auto | 1600 |
| AND UB-202 | Japan (assembled in China) | There is a WHO scale, an arrhythmia indicator, and a sound signal about measurement errors. The memory capacity is designed to store the last 90 readings. Extended cuff – 13.5-21.5 cm. Powered by 3 AAA batteries. Dimensions – 38x72x64 mm, weight – 102 g. | Auto | 1680 |
| OMRON R1 | Japan (assembled in China) | The Intellisense system is used to determine the level of forced air. Information is displayed on the LCD screen. Cuff length – 14-22 cm, power supply – batteries (2xAAA). Dimensions – 71x41x71 mm, weight – 117 g. | Auto | 1720 |
| Nissei DS-137 | Indonesia | LCD screen, powered by 4xAA batteries, rechargeable battery. The memory capacity is designed for 30 cells. Dimensions – 163x49x122 mm, weight – 354 g. | Semi-automatic | 1610 |
| Little Doctor LD-71A | China | Pointer pressure gauge, cuff 25-36 cm, built-in metal stethoscope, weight 328 g. | Mechanical | 693 |
| With connection to a smartphone | ||||
| Qardio QardioArm | China | Transfers data to a smartphone running iOS, Android via Bluetooth, so there is no screen. Easy setup, graphing capability, arrhythmia indication, memory for two users and dual measurement method. Batteries – 4 AAA types. Dimensions – 68x38x140 mm, weight – 310 g. | Auto | 8989 |
| AND UA-911BT-C | Japan | The LCD screen duplicates the readings to a smartphone via Bluetooth - there is a special A&D Connect application. Ability to save information in your personal account, 30 memory cells, powered by batteries (4xAA), network (adapter not included), arrhythmia indication. Weighs 300 g. | Auto | 3253 |
| Automatic blood pressure monitors with dual measurement | ||||
| Omron HBP-1100 | Japan (made in China) | Powered by batteries and mains. Just one memory cell. It has its own battery, adapter, and dual measurement capability. Cuff size – 22-32cm. | Auto | 9710 |
| Hartmann Tensoval Duo control | Germany | Device with double measurement on the shoulder. It is powered by 4 AAx1.5V batteries and turns off automatically 3 minutes after measurement. The memory is designed for 30 measurements for each of two users. There is a large display and a carrying case, but there is no WHO scale or arrhythmia indicator. | Auto | 4600 |
| Nissei DS-700 | Indonesia | LCD screen, powered by 4xAA, network (adapter included), memory for 30 cells, arrhythmia indication, dual measurement method, blood pressure control using two Twin Check methods. Dimensions – 135x51x140 mm, weight – 434 g. | Auto | 2430 |
Types of tonometers and criteria for their selection
Problems with blood pressure (BP) can be experienced by people of all ages. Such a pathology of the cardiovascular system as arterial hypertension is observed in approximately a third of the adult population. This is a disappointing figure, plus the older a person gets, the higher the risk of contracting this disease. You cannot ignore it - the consequences can be too serious. Among them are strokes and heart attacks, dizziness, and simply feeling unwell. Very often, the quality of life, and life itself, depend on how much the blood pressure rises or falls.In order to keep blood pressure under control and always be aware of its changes, special devices are used - tonometers. They were invented back in 1876, but have come down to our time in a completely different form. Initially it was a large rubber balloon filled with water. It, connected to a pressure gauge using a tube, was placed above the artery. About two decades later, a more familiar version appeared with a cuff that was placed on the shoulder, and to determine the pressure, they used palpation of the pulse while simultaneously taking into account the values of a mercury manometer. Naturally, obtaining more or less accurate results required some experience and skill.
Classification of modern tonometers
Modern blood pressure monitors can be classified in two different ways. First: by the method of measuring blood pressure. Second: according to the method of attachment (place of application of the cuff).
Blood pressure levels are measured using the following models:
- mechanical: when the parameter value is shown by the arrow on the dial;
- digital (automatic and semi-automatic): when the value is displayed digitally on the screen;
- mercury: when the pressure value is determined by the level of the mercury column.
There are also three ways to apply the cuff:
- on the finger;
- on the wrist;
- on the forearm.
The first criterion that guides the selection of a tonometer is the measurement method. We will dwell on it in detail, and list the rest briefly.
Mercury tonometers
Mercury models are among the very first to appear on the market, however, they differ markedly from their prototype, developed by the doctor Riva-Rocci, both in quality of execution and in accuracy of operation. Structurally, such a device consists of a mercury manometer with divisions marked on it, a bulb and a cuff. Using a bulb, air is pumped into the cuff, while simultaneously listening to tones using a stethoscope or phonendoscope. The pressure level is determined by the level of rise of the mercury column. Most often, mercury models are professional, they can be found in medical institutions.
The advantage of such a device is its very good accuracy in determining blood pressure, but the disadvantage is the pronounced toxicological properties of mercury, which greatly limits its scope of application.
Mechanical blood pressure monitors
Mechanical tonometers are deservedly popular among medical personnel even in modern medical institutions; they are most often purchased by elderly people. Structurally, such tonometers consist of a cuff, a rubber tube through which a rubber bulb is connected, a phonendoscope and a pressure gauge with an arrow and a scale. The principle of operation of a mechanical tonometer is as follows: a cuff is placed on the shoulder, air is injected using a bulb, and at this time heart rhythm tones are listened to using a phonendoscope. The measurement results can be observed on the pressure gauge screen, indicated by a moving arrow.
The advantages of such a device are accessibility (in terms of cost, this is the cheapest option), high accuracy in determining blood pressure, the least influence on the readings of external factors (hand movement, conversation during measurements, etc.), and the absence of the need for special care for the device.
The disadvantage of a mechanical tonometer is that often the accuracy of the measurement directly depends on the skills of the one who makes these measurements, as well as his accuracy of hearing and vision. The more experienced a person measures pressure, the greater the chance that the results will be as close as possible to real ones.
Semi-automatic blood pressure monitors
Unlike the two previous varieties, semi-automatic blood pressure monitors are always equipped with an electronic display that displays the measurement results. In this case, data is displayed not only on the blood pressure level, but also on the heart rate (pulse). The display in this case replaces the pressure gauge, otherwise everything here is the same as in a mechanical tonometer: a bulb with which air is pumped, a tube and a cuff. Among the additional features, such tonometers may include backlighting, a sound notification about the completion of measurements, and memory for several previous blood pressure measurements.
The advantages of semi-automatic models are that they are still affordable compared to fully automatic ones, but at the same time they provide more measurement options than mechanical ones. It turns out that they are a kind of compromise between price and set of characteristics. The presence of a display will definitely be appreciated by older people and those who suffer from hearing and/or visual impairments. What makes this device completely universal and autonomous is the lack of requirements for recharging and the use of additional power sources (batteries).
Among the disadvantages, it is worth highlighting that they still require a certain physical effort to pump air into the bulb (and not every elderly person can cope with this), and the result may be inaccurate if you do not follow the operating instructions for the device. Due to errors, it is recommended to perform two or three blood pressure measurements in a row, and then calculate the arithmetic average - this value will be as close as possible to the real one.
Automatic blood pressure monitors
Automatic blood pressure monitors are the most advanced in technical terms, but also the most expensive. There is no longer any need to pump air into them with a bulb, and the bulb itself is missing. There is only a cuff and a unit with a digital display connected to it via a tube; air is pumped automatically and without mechanical effort on the part of a person. It is these measuring devices that can be designed to be applied to the shoulder, wrist and finger. To turn them on, just press the button on the pressure gauge body, and after a few seconds information about the blood pressure value, heart rate and other indicators will appear on the screen, depending on the selected model. The additional features in them are the same as in semi-automatic models. In addition, they can have a built-in motion indicator, an indicator of the correct position of the human body during measurements, an indicator of the presence of arrhythmia and other functions.
The advantage of automatic tonometers is their ease of use, the absence of skill requirements for working with them, and the ability to measure pressure in any conditions (in a medical facility, at home, or even right on the street in emergency situations). Some models use two methods at once to improve measurement accuracy: the classical oscillometric method and the Korotkoff method.
However, they also have a lot of disadvantages: for example, low accuracy, which can only be improved by carrying out a series of sequential measurements. The high cost of such tonometers often scares off ordinary pensioners - the main target audience of these devices. Plus, due to medical reasons, they are not recommended for use by people with arterial hyperextension.
How to choose a tonometer
As already written above, the first selection criterion will be the type of tonometer, which is determined by the method of measuring blood pressure. The remaining parameters are less critical, but you still need to take them into account in order to ultimately get a truly convenient and functional device.
If a tonometer is purchased for individual use, you need to take into account all the characteristics of that person’s body. Firstly, his age. For young and middle-aged people who lead a fairly active lifestyle, we can recommend wrist-mounted blood pressure monitors; for older people, we recommend automatic and semi-automatic models. However, in the latter case, the material factor can play a significant role, in which case the choice can be made on a mechanical device.
The presence of certain cardiovascular diseases may also be an important factor that cannot be ignored. In the case of arrhythmia and tachycardia, automatic and semi-automatic models are suitable, which can sequentially take up to three measurements in a row and then compare them on the screen. With vascular atherosclerosis, only semi-automatic and automatic blood pressure monitors are suitable, since listening to heart sounds using a phonendoscope is difficult in such cases.
All models with cuffs must be selected in accordance with the hand size of the person or group of people who will use the device. The vast majority of devices have a standard cuff diameter, but you can also find some on sale that are designed for use by very obese people. The diameter of their circumference can reach 42 cm. Do not forget that the accuracy of the measurement often depends on the correct fastening of the cuff!
Pay attention to the material used to make the phonendoscope - it is better if it is metal rather than plastic. And the point here is not entirely the durability of the first, but the fact that the polymer structure worsens the sound and, accordingly, makes it difficult to work with the device. It is also better to choose a metal pressure gauge body.
If you have to measure blood pressure with a tonometer for both adults and children, you can immediately buy a model in which you can change the cuffs. It will be much more comfortable to put a baby cuff on a child’s arm. This feature is usually provided in automatic and semi-automatic models.
The presence of backlight is not critical, but a very useful feature, especially if you plan to use the tonometer at night. With it, the numbers on the screen will be much easier to understand.
Popular manufacturers and models of pressure gauges will be discussed in the next article.
09/17/2014 Soboleva Svetlana
Best lists
Let's look at a few models from additional categories:
- universal for adults and children;
- longest cuff;
- professional.
Let's move on to a description of each device.
Universal for adults and children – Little Doctor LD-71
This device is the best option for use in measuring blood pressure for children and adults. The tonometer is available only in gray color with a cuff of 250 and 360 mm. Fairly simple use, compact dimensions and a weight of only 328 grams make this model an attractive option in terms of price and quality.
Price tag: from 799 to 899 rubles.
mechanical tonometer Little Doctor LD-71
The longest cuff – B.Well WM-63S
The device presented to you has a cuff with a length of 250 - 400 mm, which is the largest indicator among devices in this segment. Due to its low cost and ease of use, this tonometer is the best option in terms of price and quality. Additionally, there is a built-in stethoscope and a phonendoscope included.
Price range from 799 to 999 rubles.
mechanical tonometer B.Well WM-63S
Professional – A&D UA-200
The device is intended for professional use, for example, use of the device in hospitals or ambulances. The cuff is made in blue color, and the circumference ranges from 220 mm to 320 mm. It is possible to measure using a phonendoscope, which is supplied in the kit, along with a cover and a supercharger.
Price: from 1099 to 1399 rubles.
mechanical tonometer A&D UA-200