The microwave oven has firmly entered into everyday life and has become one of the indispensable attributes of any apartment. This household appliance allows you to heat or cook food in a matter of minutes using radiation invisible to the eye.
But to find out where this radiation comes from and how safe it is for humans, it is necessary to understand the structure and operating principle of the microwave oven magnetron, which is a generator of high-frequency waves.
Magnetron
What are microwaves and how do they heat food?
Microwave is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength from 1 mm to 1 m. This type of radiation is used not only for domestic purposes, but also in navigation and radar systems, and also ensures the operation of cellular communications and satellite television.
Microwaves can be generated both artificially and naturally (for example, by the Sun). Another name for microwaves is ultra-high frequency radiation, or microwave.
All types of household microwave ovens have a single radiation frequency of 2450 MHz. This value is an international standard that home appliance manufacturers must strictly adhere to to ensure that their products do not interfere with the operation of other microwave devices.
Microwave radiation
The thermal effects of microwave radiation were discovered by American physicist Percy Spencer in 1942. It was he who patented the use of a device generating microwaves for cooking, thereby laying the foundation for the use of microwave ovens in everyday life.
Over the next few decades, this technology was brought to perfection, which made it possible to establish mass production of simple and inexpensive devices for quickly heating food.
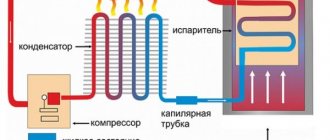
To heat any material in a microwave oven, it must contain dipole molecules, that is, molecules that have opposite electrical charges at both ends.
In food products, their main source is water. Under the influence of ultrahigh frequency radiation, these molecules begin to line up along the electromagnetic field lines, changing their direction about 5 billion times per second. The friction that arises between them is accompanied by the release of heat, which heats the food.
However, microwaves are not able to penetrate deeper than 2-3 cm from the surface of the product, so everything that is under this layer is heated due to thermal conductivity from the heated areas.
Heating food using a microwave
Magnetron design and its application
In most types of microwave technology, the generator of microwave oscillations is a magnetron. Devices similar in their principle of operation - klystrons and platinotrons - have not become so widespread. The magnetron was first used in microwave ovens in 1960. The most commonly used in technology is a multicavity magnetron, consisting of several components:
- Anode. It is a copper cylinder divided into sectors with thick metal walls. These volumetric cavities are resonators that create a ring system of oscillations. A voltage of about 4000 volts is applied to the anode.
- Cathode. It is located in the central part of the magnetron and is a cylinder containing an incandescent filament. Electron emission occurs in this part of the device. A voltage of 3 volts is supplied to the heater (filament).
- Ring magnets. Electromagnets or high-power permanent magnets located at the end parts of the device are necessary to create a magnetic field directed parallel to the magnetron axis. The movement of electrons also occurs in this direction.
- Wire loop. It is connected to the cathode, fixed in the resonator and brought to the emitter antenna. The loop serves to output microwave radiation into a waveguide, after which it enters directly into the microwave chamber.
Magnetron device
Due to their simplicity of design and low cost, magnetrons have found application in many areas, but they are most widespread:
- In microwave ovens. In addition to quickly cooking and defrosting food in household ovens, magnetrons also enable production tasks. An industrial microwave oven can perform heating, drying, melting, roasting and more. It is important to remember that the microwave cannot be turned on empty, since in this case the radiation will not be absorbed by anything and will return back to the waveguide, which can lead to its breakdown.
- In radar. The radar antenna connected to the waveguide is actually a conical feed and is used in conjunction with a parabolic reflector (dish). The magnetron produces powerful short pulses of energy with a short wavelength, part of which, when reflected, is again sent to the antenna and then to a sensitive receiver, which processes the signal and displays it on the screen.
Magnetrons in radar
Microwave oven diagram
A good example is the Samsung RE290D microwave oven. A schematic electrical diagram will help you understand how furnaces from any manufacturer work. They can differ only in specific modifications. The diagram itself is shown in the photo.
On the left side, it is noticeable that the grounding contact of the plug is connected to the housing, and it is connected from the middle point of the capacitor decoupling filter, which reduces interference from high-frequency radiation.
In the area of the power input there is a soft type fuse - FU1. To check its condition, they use electrical methods - they test the circuit with a multimeter operating in ohmmeter mode.
There is a second fuse that protects the microwave from operation in emergency mode, for example, when the door microswitches are faulty.
In order for the magnetron, the radiation source, to start “working,” the door service contacts open, and all the others close. If you turn them off, any of them, the supply voltage will be removed from the high-voltage transformer.
The circuit has thermal fuses-sensors (2 pcs.), which, depending on the temperature of the magnetron housing and the working chamber, open and close. The first one has periodic work. It protects the magnetron from overheating. The second one is triggered if the fan is faulty or the ventilation holes are clogged.
Microwave Samsung RE290D
The safety relay contact provides connection to the electric motors of the timer and cooling fan. If the Monitor Fuse blows, the relay coil will fail.
The switch responsible for selecting power is located on the timer. He, following the algorithms, removes the voltage from the magnetron circuit.
Resistor R1 briefly reduces the starting current of the transformer. This requires a working Inrush Relay contact.
Its task is to limit the pulse caused by the discharge of the capacitor (it can receive a charge before it turns on). This ensures that the microwave oven starts smoothly.
The power circuit of this oven from Samsung is simple for those who understand it. The main difference in microwave ovens is the electronic units, with different designs and functionality.
Magnetron operating principle
The operation of a microwave oven is based on the conversion of electrical energy into ultra-high frequency electromagnetic radiation, which sets in motion water molecules in food. Dipole molecules, constantly changing direction, generate heat, which allows you to quickly heat foods while maintaining their beneficial properties. The device that generates microwaves is a magnetron.
A magnetron, in fact, is an electric vacuum diode that uses the phenomenon of thermionic emission. This phenomenon occurs during the heating of the surface of the emitter or cathode. Under the influence of high temperature, the most active electrons tend to leave its surface, but this will only happen when voltage is applied to the anode. In this case, an electric field arises, and electrons begin to move towards the anode, moving along its field lines. If electrons find themselves in the zone of action of a magnetic field, then their trajectories deviate towards the direction of the field lines.
Vacuum diode
The magnetron anode has the shape of a cylinder with a system of cavities, or resonators, inside which there is a cathode with an incandescent filament. Two ring magnets located at the edges of the anode create a magnetic field inside the anode, due to which the electrons do not move directly from the cathode to the anode, but change their trajectory, rotating around the cathode. Near the resonators, electrons give them part of their energy, which leads to the formation of a powerful microwave field in their cavities, which is brought out using a wire loop connected to the emitter antenna.
To activate the magnetron, it is necessary to apply a high voltage of about 3-4 thousand volts to the anode. Therefore, the magnetron is connected to the household electrical network via a high-voltage transformer. In addition, the microwave oven circuit includes a waveguide that transmits radiation inside the chamber, a switching circuit, a control unit, as well as protection and cooling elements. In addition, the internal walls of the chamber and a thin metal mesh on the device door prevent radiation from escaping beyond its boundaries.
Magnetron connection diagram
The main element of a conventional microwave oven is a magnetron, a vacuum device for generating microwave radiation.
His older relatives are in all sorts of radars and radar systems. It is due to the microwaves emitted by it that microwaves heat up food: the frequency is chosen in such a way that it causes resonance phenomena in water molecules, which are contained in almost any food, and they begin to warm up. Due to the high power of the magnetron, the heating is very noticeable, which gives the desired effect. The magnetron can, of course, be removed from this very stove. It looks like this funny contraption with a powerful radiator. The pin sticking out from above is the actual microwave emitter, from which the radiation comes. Typical power is about 700-800 watts, which, I must say, is a lot and a lot and will easily boil the immature brains (or rather, the eyes) of such an emitter caught in the focus. Fortunately, the radiation from the magnetron pin is omnidirectional and therefore relatively safe as long as you don't get too close.
If you tear off the radiator, you will be left with a rather small copper-ceramic piece of crap with two magnets. If you take it further apart and saw it in half, you will find a rather curious chamomile-like structure inside. For specific principles of its operation and the generation of microwaves there, I refer you to more specialized sources; this is no longer the place here.
By the way, an interesting feature of the magnetron: it has a negative voltage going to the filament (cathode), and the body, also known as the anode, is grounded. From the same microwave you can completely tear out the power supply for the magnetron - MOT, capacitor and diode, and, in fact, connect it - the same way it was connected in the stove. The filament winding of the MOT feeds the filament, the housings of the MOT and the magnetron are connected, the capacitor and diode form a shifter, and it is connected by a hot lead (the connection point between the capacitor and the diode) to one of the filament terminals of the magnetron (which is why the filament winding of the mot is made of a high-voltage wire).
When turning it on, you should still be careful, do not turn it on for a long time and protect your eyes, especially when starting it indoors. If you place a sharp piece of metal on top of the output, you can get a 2.4 GHz torch. Only this output burns out very quickly.
But just having fun with a magnetron is quite boring. It is much more interesting to adapt an antenna to it to obtain a more or less directed radiation flux. A parabolic dish would be ideal. But the diameter required is about five meters. A little worse, but also not bad, is the “horn” type antenna, but its manufacture is quite tedious and it turns out to be quite bulky, although, of course, smaller than a parabola. I eventually settled on a can antenna (Google “cantenna”), which gained love among fans of Wi-Fi amplification. Since the magnetron operates at exactly the same frequency as Wi-Fi, you can simply consider the can as for a Wi-Fi antenna. The gain from it is not very high, the shape of the flow also leaves much to be desired, but it can very pleasantly illuminate gas-discharge devices, boil the eyes of mice with small volumes of water, and reset the neighbor’s wifi router. By the way, the camera goes out a meter from the antenna canister. For better cooling, a cooler was installed for the magnetron, since the latter gets quite hot during operation.
Share on social media networks
There are no tags.
How does a magnetron affect microwave power?
Most modern manufacturers of microwave ovens offer the ability to select the power of the device. This parameter, in turn, determines the operating mode (defrosting or heating) and the speed of heating the food. However, the design features of the magnetron do not allow reducing its power, therefore, to reduce the heating intensity, power is supplied to it at certain intervals. These pauses in the operation of the magnetron can be noticed if you turn on the microwave at medium power and listen to the sound of its operation.
Not long ago, some manufacturers of household appliances announced the appearance of a number of models of microwave ovens with an inverter power supply circuit. The use of this scheme made it possible not only to increase the amount of usable space in the chamber by reducing the dimensions of the emitter, but also to reduce the power consumption of the device. Unlike conventional models, the heating temperature in inverter-type furnaces changes smoothly, but their cost is an order of magnitude higher.
Is it possible to replace it yourself?
Any type of magnetron for LG microwave ovens can be replaced with a similar one for another. Similarly, you can replace the magnetron for a Samsung microwave oven with an element of suitable power from another company. If a model of a household microwave oven was produced a very long time ago, then it is very difficult to find a part of the corresponding brand. Perhaps the manufacturer has already discontinued this type.
But even if you know the principle of operation of a magnetron, you should not attempt to repair such equipment at home yourself.
You can purchase a magnetron for the 2M218 JF Daewoo microwave oven yourself by ordering it in specialized stores or directly from the manufacturer. It costs about 2 thousand rubles.
Magnetron cooling and protection
During operation, the magnetron generates a large amount of heat, so a radiator is installed on its body. Since overheating is the main cause of magnetron failure, other methods are used to protect it:
- Thermal relay. This device is used to protect the magnetron, as well as the grill, if the model has one. The thermal fuse is equipped with a bimetallic strip that can be adjusted to a specific temperature. If this value is exceeded, it bends and opens the power circuit.
- Fan. It not only blows cool air onto the magnetron radiator, but also performs a number of other useful functions, such as cooling the electronic components of the device, circulating air inside the chamber during grill operation, and also removing hot steam out through special holes.
- Locking system. Several microswitches control the position of the microwave door, preventing the magnetron from turning on when it is open.
Thermal relay
Is it possible to replace the magnetron
The main advantage of modern magnetrons for household microwave ovens is their interchangeability. Magnetrons produced by other companies will be suitable for different models of microwave ovens, so they can be changed if necessary. In this case, the only necessary requirement will be power matching. You can buy a magnetron in many electronics stores, but in order to make the right choice, you need to understand its parameters and labeling. The following magnetron models are most often installed in microwave ovens:
- 2M 213 (600 W rated power and 700 W under load);
- 2M 214 (1000 W);
- 2M 246 (1150 W – highest power).
Even after studying all the necessary parameters of this device, it is not recommended to replace the magnetron at home. Firstly, it will be quite difficult to remove it yourself, and secondly, only a qualified specialist can ensure its safe operation after installation.
Standard magnetron configuration
Diagnosis of faults and causes of their occurrence
Replacing a magnetron can require quite significant financial costs, so before buying a new device, you need to diagnose the old one to make sure that it is really faulty. The test can be done at home using a regular tester. To do this you will need:
- Disconnect the microwave from the electrical outlet.
- Remove the protective cover and conduct a visual inspection of the part.
- “Ring” the main elements of the printed circuit board using a tester or “multimeter”.
- Inspect the thermostat.
Diagnostics
At the end of the diagnostics, conclusions can be drawn about the malfunction of certain parts. The main reasons for magnetron failure include the following:
- Vacuum tube cap is faulty. You can replace it yourself by simply selecting a similar cap from another magnetron. The seats of such caps have a standard configuration.
- Heater breakage. If you turn on an empty microwave or load it incorrectly, the magnetron will overheat, which can lead to excessive heating of the filament and its breakage. To diagnose it, it is necessary to measure the resistance between the legs of the capacitor. If its value is within 5-7 Ohms, then the heater is working.
- Breakdown of the feed-through capacitor. If the tester does not show an “infinite” resistance value between its contacts, then the capacitor must be replaced.
Possible faults
The internal circuit of the magnetron contains many parts, and if a breakdown occurs, the reason may lie precisely in them. It happens that one of the parts has become unusable, but it affects the operation of the entire lamp. You should understand the cause of the malfunction and solve the problem at home. We will tell you exactly how later.
- The metal cap is responsible for maintaining the vacuum inside the pipe. It often breaks and requires a new replacement;
- The radiator may become unusable if the part burns out;
- The filament may break due to overheating. To detect such a malfunction, a special device is needed;
- The filter may also stop functioning normally; it should be checked with a tester. A serviceable element will show infinity, and a broken one will show numerical resistance;
- Change in the tightness of a part due to overheating;
- Malfunction of the high-voltage diode;
- High voltage capacitor malfunction;
- Broken fuse contacts, the main task of which is to prevent overheating.
It will be interesting➡ What are triodes and where are they used