| Place | Name | Characteristics in the rating |
| The best indoor antennas with amplifier |
| 1 | Thomson ANT1425 | Best amplifier |
| 2 | Hyundai H-TAI220 | High build quality. Ease of setup |
| 3 | Selenga 105A | The optimal choice for signal reception in any conditions |
| 4 | REMO BAS-5310 Horizon USB | The most attractive price |
| 5 | Perfeo Forward | The amplifier does not require a network connection |
| The best indoor antennas for a summer residence |
| 1 | Delta K131A.03 | Optimal ratio of reception quality and price |
| 2 | REMO BAS-5324-USB Diagram | Buyer's Best Choice |
| 3 | LUMAX DA1502A | Universal model |
| 4 | Delta K331A.02 | High-quality data transfer |
| 5 | Antenna DENN DAA238 | Reliable reception of a remote signal. Elegant design |
| The best indoor antennas for receiving a digital signal |
| 1 | REMO BAS-5107-5V Mini Digital | No need for an external adapter |
| 2 | Antenna BBK DA03 | Favorable price offer. Satisfactory build quality |
| 3 | Delta Digit.5V | The best choice for working with a digital set-top box |
| 4 | Locus L 942.10 CAYMAN | Steel body. For a reliable reception area |
| 5 | GAL AR-007 | The best combination of price and performance |
DVB-T2 or an antenna for receiving a digital signal for watching TV will be the focus of our attention. To this day, the best antenna is the one on the roof of your house, but technology has moved far forward, making it possible to install signal receivers indoors. The best choice for a country house or cottage would be a satellite dish or a giant antenna with many receiving elements.
In general, the antennas we are considering are designed primarily to receive signals from decimeter waves, that is, from 400 to 800 MHz. They were sold before, but their setup and design were associated with imperfect technology and a number of installation problems. Modern communication quality has lowered the requirements for receiving elements. We have selected for you the top 10 best indoor antennas for connecting and watching quality TV.
Features of television signal propagation
The distance over which the signal is transmitted in the UHF range does not have a large coverage area. It is much less than in the meter range.
For example:
If you have used a radio, you may have noticed that you cannot catch distant foreign radio stations in the FM or VHF bands, but only those nearby, local ones. But on the other hand, you can catch a whole bunch of foreign ones in the CB or HF bands.
This is because medium and short waves, like meter ones, propagate over long distances, and ultrashort waves, like UHF, over short distances.
This disadvantage of the UHF range for digital TV is compensated by the location and number of television transmitters - by analogy with cell towers, there are many of them.
Also keep in mind that the television signal is perfectly reflected from objects encountered along the way.
This allows you to receive broadcasts when it is not possible to point the antenna towards the TV tower. Or there are obstacles to the direct passage of the signal.
Look around! Is it possible to receive a reflected signal?
So if you choose the right antenna and install it correctly, you will surely achieve success.
An example of how to receive a reflected signal
What else should you consider when choosing an antenna?
Conditions for receiving a television signal vary greatly in different places and these conditions must be taken into account when choosing an antenna.
Here are some factors that will determine which antenna you need to purchase and how to install it.
- The power of the television transmitter and its signal coverage area.
- Terrain - mountains, lowlands, plains.
- Standing nearby and blocking the antenna towards the tower are tall, dense trees.
- The presence of high-rise buildings and your location in relation to these buildings and the tower.
- The floor you live on - the higher you are, the simpler the antenna you will need.
- Possibility or impossibility of turning the antenna towards the transmitting tower.
Which antenna is suitable for DVB-T2 digital television
With the advent of digital terrestrial television, many people have questions related to the choice of antenna for DVB-T2. For example!
- Can I use my old antenna, if I had one?
- Is an antenna of the “Lattice” type, also known as “Polish”, suitable for this?
- Do I need an antenna with or without an amplifier?
- Which antenna to choose if there is a question about purchasing a new one?
- Is the advertised “Key to Free TV” antenna necessary?
- How to set up an antenna for digital television.
Let's first figure out what kind of antennas there are.
Antennas of the meter (MV) and decimeter (UHF) ranges are used to receive television signals. There are broadband antennas, this is a “hybrid” when elements of the MV and UHF bands are used in the antenna design.
These antennas are easy to distinguish from each other by size.
The MV range has longer elements. Everything is according to the name.
So in MV antennas the elements are approximately half a meter to one and a half meters in length.
And the elements of the UHF antenna are only about 15 to 40 cm long.
It is the UHF antenna that is needed for digital terrestrial television.
VHF Antenna
Example of a UHF antenna
Broadband antenna, MV and UHF ranges.
Array antenna
Broadband antenna "Hummingbird"
So - To receive digital terrestrial television you need a UHF antenna, i.e. antenna with short elements. Or broadband.
Now you can evaluate whether your old antenna is suitable for receiving television in the DVB -T2 format. The only question that remains open is its serviceability and effectiveness in your area.
In addition to dividing by received ranges, antennas are also divided into...
Indoor and outdoor (External) - I think everything is clear with the application here.
And also active and passive - more on that a little later.
Well, a brief excursion into the difficult topic of terrestrial antennas has been carried out. Let's continue...
How does digital work?
Digital television is streaming with the ability to broadcast channels on the same frequency. This is very convenient, as it helps solve a number of problems that arose in connection with analogue broadcasting:
- due to the fact that the channels are on the same frequency, quick tuning of the TV has become possible;
- lack of bureaucracy, since now each channel does not need to acquire a special license;
- repeaters are simpler in design than massive analog towers;
- a noticeable improvement in image quality and the absence of interference on the TV screen;
- switching from analog to digital is accessible and quite affordable;
- the image is available even with a weak signal.
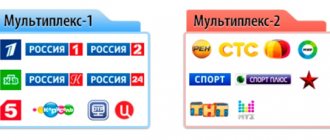
The signal from the broadcasting station is transmitted using ground stations - repeaters. Each tower provides packet broadcasting of 10 channels, collected in a multiplex. The user just needs to buy an antenna that will pick up the required signal. If you are using an old TV, then you still need to purchase a set-top box for it, and newer models do not need such an addition, since they themselves are able to pick up a digital TV signal.
Terrestrial digital television is provided to users absolutely free of charge, without fees or monthly payments.
Active and passive antennas - what is the difference?
Antennas of any type can be either active or passive.
Passive antennas are those that amplify the signal only due to their design, without the use of electronic amplifiers; such antennas are used in areas with a strong signal.
Active antenna - has an amplifier in its design; such an antenna needs to be connected to a power source. The amplifier helps to increase the level of the received signal in areas of poor reception.
How to connect power to an active antenna amplifier, several ways
Antenna amplifiers are powered by 12 or 5 volts. But recently, more and more, manufacturers are focused on producing antennas with five-volt power supply.
And there is a reason for this! Such antennas are easier to connect for those who use a DVB-T2 set-top box. How to choose a console
Three connection methods
A) Use a special power supply with a separator
which produces the voltage corresponding to your amplifier.
The purpose of a separator is to separate. It passes voltage to the antenna, but does not pass it to the TV socket. However, this does not interfere with the signal from the antenna amplifier entering the TV.
B) If a DVB-T2 set-top box is used. A voltage of 5 volts can be supplied directly from the set-top box. Moreover, for any amplifiers, both 5 and 12 volts.
This does not require any additional wire, power supply, etc. The voltage is 5 volts, from the antenna socket of the set-top box, directly through the antenna cable, it will go to the amplifier.
You just need to turn on this power directly from the set-top box menu. Go to the settings section and find the item “Antenna power ON-OFF”, select ON, and exit the menu (the names of these items may differ in different models of set-top boxes)
B) If you have an LCD TV with a built-in DVB-T2 tuner, then in addition to the method under letter A) you can do the following.
You will have to purchase a special adapter to power the amplifier from any USB port; first of all, consider the USB port of the LCD TV itself. But you can connect to any charger with a USB output